Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It can be spread through oral, anal, or genital contact with someone who has the virus. While it is possible to treat genital herpes, it is incurable and there are potential long-term health risks associated with not treating it. In this article, we will discuss the increased risk of other STDs when genital herpes goes untreated.
It is important to understand the risks associated with leaving genital herpes untreated in order to make an informed decision about your health. We will explain what an untreated infection could mean for your future health, as well as the risks of other STDs that could arise from leaving it untreated. In addition, we will look at the available treatments and provide advice on how to reduce your risk of transmitting the virus to someone else. Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is highly contagious and can be passed from one person to another through skin-to-skin contact.
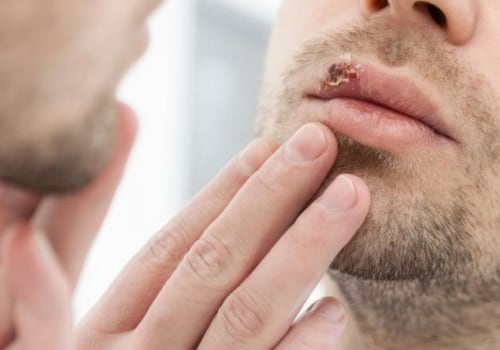
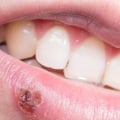
Symptoms of genital herpes may include painful blisters on the genitals, anus, or rectum, as well as sores, itching, and burning. However, it is possible to have genital herpes without showing any symptoms at all, making it difficult to know when someone has the virus. The virus is usually spread through direct contact with the infected area, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It can also be spread by sharing objects such as towels and clothing, although this is less common. If someone has genital herpes, they can prevent passing it to their sexual partner by using condoms or other barrier methods during sexual activity. Symptoms of genital herpes may include painful blisters on the genitals, anus, or rectum, as well as sores, itching, and burning. However, it is possible to have genital herpes without showing any symptoms at all, making it difficult to know when someone has the virus. The virus is usually spread through direct contact with the infected area, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It can also be spread by sharing objects such as towels and clothing, although this is less common. If someone has genital herpes, they can prevent passing it to their sexual partner by using condoms or other barrier methods during sexual activity.
It is also important to avoid contact with any active sores or blisters.
Increased Risk of Other STDs
Untreated genital herpes can have many risks that can affect you and your partner's health. For example, people who have genital herpes are at an increased risk of contracting other STDs such as HIV or syphilis. This is due to their weakened immune system which makes them more susceptible to infection. Additionally, someone with untreated genital herpes can pass the virus to their sexual partner even if they are not showing any symptoms at the time. Another potential complication associated with untreated genital herpes is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs that can cause pain and inflammation in the abdomen. It is also a risk factor for infertility in women. Additionally, there is an increased risk of HIV transmission when someone has untreated genital herpes due to the immune system's weakened state. Finally, untreated genital herpes can cause other complications such as cold sores on the mouth or face, eye infections, and meningitis. In some cases, untreated genital herpes can even lead to death.
Therefore, it is important to take steps to prevent and treat the virus to reduce these risks.
How is Genital Herpes Transmitted?
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It can be passed from one person to another through direct contact with a herpes sore or secretions from the genitals, mouth, or anus. It can also be passed from one person to another through contact with infected skin or mucous membranes, such as during sexual activity. The virus is most easily spread when a person has open sores or blisters.However, the virus can still be transmitted even when there are no visible signs or symptoms. This is why it is important to practice safe sex and get tested regularly if you are sexually active. In order to prevent the spread of genital herpes, it is important to practice safe sex. This includes using condoms and dental dams to reduce skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity. It is also important to avoid sexual contact if either partner has an active outbreak of genital herpes.
It is also important to get tested for STIs regularly and to be honest about your sexual history with your partner. This will help ensure that both partners have an accurate understanding of their status and can take steps to prevent transmission. By following these preventive measures, you can help reduce your risk of transmitting genital herpes to your partner.
What Are the Risks of Untreated Genital Herpes?
Having untreated genital herpes can present a number of risks to an individual's health, as well as to the health of any partners they may have. One of the primary risks associated with untreated genital herpes is the increased likelihood of contracting other sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Studies have shown that individuals with untreated genital herpes are at a greater risk of contracting other STDs, such as HIV, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis.In addition to the increased risk of contracting other STDs, untreated genital herpes can also cause a number of potential complications. These complications can range from mild to severe, and can include skin infections, vision problems, inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), and even death. It is important for individuals with untreated genital herpes to be aware of these potential complications and discuss them with their doctor if any signs or symptoms develop. When it comes to passing on the virus to sexual partners, individuals with untreated genital herpes are at risk of transmitting the virus even when they do not have any visible signs or symptoms.
This is known as “asymptomatic shedding” and can occur even when no lesions or blisters are present. To reduce this risk and protect partners from potential infection, individuals with untreated genital herpes should always practice safe sex and use condoms during intimate contact. Untreated genital herpes can have serious consequences if left untreated, including an increased risk of contracting other STDs, the potential for passing it to a partner, and other potential complications. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have genital herpes, and to practice preventive measures such as proper hygiene and protection when engaging in sexual activity. By understanding the risks associated with untreated genital herpes, you can take steps to protect yourself and your partners from harm. Knowing the symptoms and seeking medical help as soon as possible can make all the difference in preventing further spread of the disease.