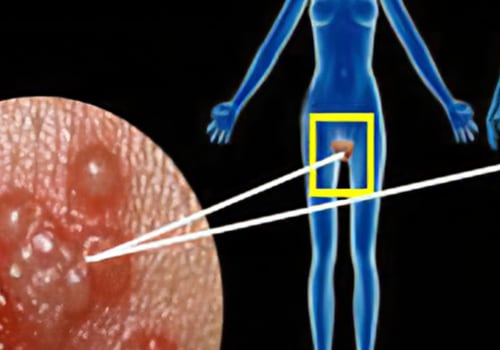
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. It can cause recurrent outbreaks of painful sores on the genitals and other parts of the body, as well as long-term health complications. While genital herpes is a common condition, many people do not understand the risks associated with it and how to best protect themselves. This article will explore the risks of recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications of genital herpes, helping readers to better protect their health. Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus.
It can cause recurrent outbreaks of painful blisters and sores in the genital area, leading to many risks associated with recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications. These risks can include physical health risks, psychological health risks, and social risks. Fortunately, there are ways to manage and reduce these risks, such as making lifestyle changes, using medications, trying home remedies, and practicing stress management techniques. It can cause recurrent outbreaks of painful blisters and sores in the genital area, leading to many risks associated with recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications. These risks can include physical health risks, psychological health risks, and social risks. Fortunately, there are ways to manage and reduce these risks, such as making lifestyle changes, using medications, trying home remedies, and practicing stress management techniques.
Types of Risks
Physical health risks associated with recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications of genital herpes include skin irritation, inflammation, pain, and increased risk of other infections due to the open sores.It is important to seek medical care if any of these symptoms occur. Psychological health risks can include depression and anxiety due to the stigma attached to genital herpes. Social risks can include difficulties with relationships and intimacy due to the fear of transmitting the virus.
Managing and Reducing Risks
When it comes to managing and reducing the risks associated with recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications of genital herpes, lifestyle changes are key.It is important to practice safe sex by using condoms, limit alcohol intake, maintain a healthy diet, get adequate sleep, and practice stress management techniques such as meditation or yoga. Additionally, medications may be prescribed by a doctor to reduce the severity and frequency of outbreaks. Home remedies such as applying cold compresses to the affected area or taking warm baths may also provide relief from symptoms.
Diagnosis & Treatment Options
It is important to seek medical care if any symptoms associated with genital herpes appear.A doctor can diagnose genital herpes with a physical exam and laboratory tests. Treatment options for genital herpes depend on the severity of the outbreak. Antiviral medications can reduce the severity and frequency of outbreaks, while topical medications can help reduce symptoms. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue or sores that do not respond to other treatments.
Transmission Risks
It is important to be aware that genital herpes can be transmitted through sexual contact or contact with infected skin or mucous membranes.It is important to practice safe sex by using condoms or dental dams during sexual activity, as well as avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks. Additionally, it is important to avoid sharing items such as towels or toothbrushes with someone who has genital herpes.
Myths & Misconceptions
There are many myths and misconceptions about genital herpes that can lead to feelings of shame or fear. It is important to remember that genital herpes is a common condition and is not a sign of moral failure or personal weakness. It is also important to remember that most people who have genital herpes do not experience any symptoms.Support Resources
If you are struggling with recurrent outbreaks or long-term complications of genital herpes, there are many support resources available.These include online support groups, counseling services, and support from family and friends. It is important to reach out for help if you are feeling overwhelmed or discouraged.
Physical Health Risks
Recurrent outbreaks of genital herpes can cause a number of physical health risks. The most common symptoms associated with genital herpes include pain, itching, and burning sensations in the genital area. These symptoms can be very uncomfortable and can interfere with everyday activities.In addition, recurrent outbreaks of genital herpes can also increase the risk of developing other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). This is because the open sores caused by the virus make it easier for other STIs to enter the body. Finally, recurrent outbreaks of genital herpes can also lead to more serious health complications such as meningitis and organ damage. Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord, and can cause severe headaches, fever, confusion, and even death if left untreated.
Organ damage can occur if the virus spreads from the genital area to other parts of the body, such as the lungs or liver. It is important to be aware of the potential physical health risks associated with recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications of genital herpes. While these risks cannot be eliminated entirely, they can be minimized through proper treatment and management.
Psychological Health Risks
Genital herpes can have a significant impact on an individual's psychological health. People living with genital herpes may experience feelings of stress, anxiety, guilt, shame, embarrassment, or low self-esteem. These feelings can lead to depression and other mental health issues.Additionally, genital herpes can have an effect on relationships, as it may be difficult to talk to partners about having the virus. Infection with genital herpes can lead to feelings of fear and insecurity. People may worry about transmitting the virus to their sexual partners or fear that they will never be able to have a fulfilling sexual relationship. This can lead to decreased libido and difficulty achieving sexual satisfaction. The stigma associated with genital herpes may also contribute to psychological health issues. People may feel embarrassed or ashamed about having the virus and may be reluctant to talk about it with friends or even healthcare professionals.
This can lead to social isolation and further mental health problems. It is important for people living with genital herpes to remember that they are not alone. There are support groups available and healthcare professionals who can help manage the virus and provide emotional support. Treatments can be used to reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks, which may also help to improve psychological health.
Managing and Reducing Risks
Managing and Reducing Risks of Genital HerpesGenital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus, which can cause recurrent outbreaks of painful blisters and sores in the genital area. While these outbreaks can be treated and managed, there are also risks associated with recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications of genital herpes.Fortunately, there are ways to manage and reduce these risks. One way to help manage and reduce the risks associated with genital herpes is to make lifestyle changes. These include getting enough rest, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol intake, quitting smoking if applicable, and avoiding triggers such as sun exposure or stress. Additionally, it is important to take medications as prescribed by a doctor, try home remedies such as ice packs or topical creams, manage stress through relaxation techniques or counseling, and seek support from family members or support groups. Making these lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications of genital herpes. It is important to remember that everyone's experience with the virus is different, so it is best to discuss any lifestyle changes with a healthcare professional to find out what works best for you. Fortunately, there are ways to manage and reduce these risks. One way to help manage and reduce the risks associated with genital herpes is to make lifestyle changes. These include getting enough rest, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol intake, quitting smoking if applicable, and avoiding triggers such as sun exposure or stress. Additionally, it is important to take medications as prescribed by a doctor, try home remedies such as ice packs or topical creams, manage stress through relaxation techniques or counseling, and seek support from family members or support groups. Making these lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications of genital herpes. It is important to remember that everyone's experience with the virus is different, so it is best to discuss any lifestyle changes with a healthcare professional to find out what works best for you.
Social Risks
Genital herpes is a highly stigmatized infection, and when disclosed, can lead to social consequences.People living with genital herpes may face discrimination, judgment, and negative reactions from their peers. Disclosure of a genital herpes diagnosis can be difficult due to the social stigma associated with it, and this can lead to feelings of shame, embarrassment, and guilt. In some cases, a person living with genital herpes may be limited in terms of access to certain activities or events. This could include activities such as swimming or attending a spa, where the risk of transmitting the infection to others is high. Other activities such as attending a college or university may also be affected if there is a risk of transmitting the infection to others. In addition to the physical symptoms of genital herpes, many people living with the infection may experience psychological effects.
These can include depression, anxiety, and fear of relationships and intimacy. People living with genital herpes may also have difficulty communicating their diagnosis to a partner or potential partner. The social risks associated with recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications of genital herpes can be managed and reduced. People living with genital herpes should seek out support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals. They should also be open and honest about their diagnosis with any potential partners, to ensure that both parties are comfortable and aware of the risks associated with transmission. In conclusion, genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus that can cause recurrent outbreaks of painful blisters and sores in the genital area.
These recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications can result in physical health risks, psychological health risks, and social risks. However, these risks can be managed and reduced by making lifestyle changes, taking medications, using home remedies, engaging in stress management techniques, and utilizing support resources. It is important to talk to a healthcare provider for more information on how to best manage these risks. These recurrent outbreaks and long-term complications can result in physical health risks, psychological health risks, and social risks. However, these risks can be managed and reduced by making lifestyle changes, taking medications, using home remedies, engaging in stress management techniques, and utilizing support resources. It is important to talk to a healthcare provider for more information on how to best manage these risks.