Have you ever been in contact with an infected person's saliva or skin? If so, you may have unknowingly been exposed to a contagious virus. Knowing the risks associated with contact with an infected person's saliva or skin is essential for protecting yourself and others from infection. In this article, we'll explore the dangers of contact with an infected person's saliva or skin and how to protect yourself from potential infection. We'll discuss what viruses can be transmitted through contact with an infected person's saliva or skin, signs and symptoms of infection, and steps to take if you think you've been exposed. We'll also provide tips on how to reduce your risk of becoming infected with a virus.
Oral Herpes
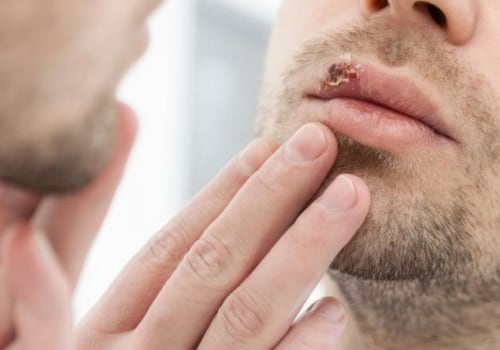
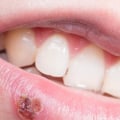
is a contagious viral infection caused by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1).The virus is usually passed from person to person through saliva or skin contact, making contact with an infected person's saliva or skin one of the most common ways to contract oral herpes. Symptoms of oral herpes can range from mild to severe, and can include cold sores, fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes and mouth ulcers. The best way to reduce the risk of becoming infected with oral herpes is to avoid contact with an infected person's saliva or skin. If you must come into contact with someone who is infected, it's important to practice good hygiene.
This includes washing your hands frequently, avoiding close contact with the infected person and avoiding sharing food, drinks or personal items. If you do come into contact with an infected person's saliva or skin, there are ways to protect yourself from infection. Wearing protective gloves and avoiding direct contact with saliva or skin can help reduce the risk of infection. Additionally, avoiding activities that may cause saliva to be shared, such as kissing, can also reduce the risk of infection. If you become infected with oral herpes, it is important to seek medical attention.
Treatment options depend on the severity of symptoms, but may include antiviral medications, topical ointments, pain relievers and other medications. Additionally, there are natural remedies that may help reduce symptoms and speed up recovery time. Understanding contact with an infected person's saliva or skin is important in order to reduce the risk of contracting oral herpes. Practicing good hygiene and avoiding contact with an infected person's saliva or skin is the best way to protect yourself from infection.
If you do become infected, there are treatments available that can help reduce symptoms and speed up recovery time.
Treating Oral Herpes
Oral herpes can be treated with antiviral medications such as acyclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir. These medications work to reduce the duration and intensity of symptoms caused by oral herpes by preventing the virus from replicating. The length of treatment depends on the severity of the infection and how long the patient has been experiencing symptoms. The side effects associated with these medications are usually mild and may include nausea, headache, and diarrhea.In some cases, more serious reactions such as increased blood pressure or liver damage have been reported. People with a weakened immune system should speak to their doctor before taking antiviral medications. It typically takes several days for antiviral medications to start working. The virus may still be present in the body even after symptoms have subsided.
It is important to finish the full course of treatment as prescribed by your doctor, even if your symptoms are gone.
Reducing Your Risk of Infection
Coming into contact with an infected person's saliva or skin is one of the most common ways to contract oral herpes, a contagious viral infection. To reduce your risk of infection, it is important to take measures to avoid contact with an infected person. This includes not kissing or sharing utensils or towels with someone who may have herpes. You should also wash your hands frequently and avoid touching your eyes, mouth, or nose after coming into contact with anything that may be contaminated. It is also important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of oral herpes in others.These can include cold sores, blisters, pain or itching around the mouth and lips, or swollen glands. If you notice any of these signs in someone you come into contact with, it is best to avoid them and take extra precautions to protect yourself.
Risk Factors for Infection
Coming into contact with an infected person's saliva or skin is one of the most common ways to contract oral herpes, a contagious viral infection. There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of infection, such as kissing, sharing utensils and towels, and other types of contact. Kissing is one of the most common ways to spread oral herpes.When an infected person kisses someone, the virus can be transmitted through saliva. Sharing utensils and towels can also spread the virus, as can other forms of physical contact such as hugging or shaking hands. It is more likely to be spread through saliva than skin because the virus is able to survive in saliva for longer periods of time than on skin. Saliva also contains higher concentrations of the virus than skin.
The virus is also able to survive on surfaces such as utensils and towels for a longer period of time than on skin. It is important to be aware of the risks associated with coming into contact with an infected person's saliva or skin. Taking proper precautions, such as avoiding contact with saliva and washing hands often, can help reduce the chances of infection.
Protecting Yourself from Infection
Coming into contact with an infected person's saliva or skin is one of the most common ways to contract oral herpes, a contagious viral infection. To protect yourself from infection, it is important to take certain precautions.These include using condoms for oral sex, avoiding contact with an infected person, and recognizing symptoms of infection in others. One of the best ways to protect yourself from infection is to use condoms for oral sex. Condoms provide a protective barrier that can help reduce your risk of contracting the virus. Additionally, condoms can help reduce the risk of transmission from one partner to another. It is also important to avoid contact with an infected person. If you know someone who has been diagnosed with oral herpes, it is best to avoid direct contact with them.
This includes kissing, sharing drinks or food, and any other type of physical contact. It is also important to be able to recognize the symptoms of infection in others. Common symptoms include fever blisters or sores in the mouth and throat, swollen glands, and difficulty swallowing. If you notice any of these symptoms in someone else, it is important to take steps to protect yourself. Taking the necessary precautions can help reduce your risk of contracting oral herpes. By using condoms for oral sex, avoiding contact with an infected person, and recognizing symptoms of infection in others, you can help protect yourself from infection. This includes kissing, sharing drinks or food, and any other type of physical contact. It is also important to be able to recognize the symptoms of infection in others. Common symptoms include fever blisters or sores in the mouth and throat, swollen glands, and difficulty swallowing. If you notice any of these symptoms in someone else, it is important to take steps to protect yourself. Taking the necessary precautions can help reduce your risk of contracting oral herpes. By using condoms for oral sex, avoiding contact with an infected person, and recognizing symptoms of infection in others, you can help protect yourself from infection.
What is Oral Herpes?
Oral herpes, also known as cold sores or fever blisters, is a contagious viral infection that affects the lips and mouth.It is caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) and is spread through contact with an infected person's saliva or skin. The virus causes painful sores or blisters on the lips, gums, tongue, roof of the mouth, and inside the cheeks. Other symptoms may include a fever, headache, and swollen glands. It is important to note that oral herpes is different from genital herpes. Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the same virus.
However, it is spread through sexual contact and results in blisters or sores on or around the genitals or rectum.
Oral Herpes
is a contagious viral infection that affects the lips and mouth. Symptoms may include painful sores or blisters on the lips, gums, tongue, roof of the mouth, and inside the cheeks. Other symptoms may include a fever, headache, and swollen glands.Genital Herpes
is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the same virus.However, it is spread through sexual contact and results in blisters or sores on or around the genitals or rectum. Oral herpes is a contagious viral infection that is most commonly contracted through contact with an infected person's saliva or skin. This article has explored the risks associated with this type of contact, and how to reduce those risks. It is important to remember that protection can be taken to reduce the likelihood of infection, and that treatment is available for those who become infected.