Genital herpes is a contagious and incurable sexually transmitted disease (STD). It is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and can cause painful sores, itching, and burning sensations. While there is no cure for genital herpes, there are measures you can take to reduce the risk of spreading the infection to yourself and others. In this article, we'll discuss some key strategies for preventing the spread of genital herpes infection.
Genital Herpes
is a highly contagious sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).It is important to understand how to prevent the spread of genital herpes in order to reduce the risk of infection. This article will discuss the complications associated with genital herpes, as well as preventive measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of transmission.
Types of HSV
- There are two types of HSV, type 1 and type 2.Type 1 usually affects the mouth, lips, and face and is the cause of cold sores, while type 2 usually affects the genital area. Both types of HSV can cause genital herpes, but type 2 is more common.Symptoms of Genital Herpes
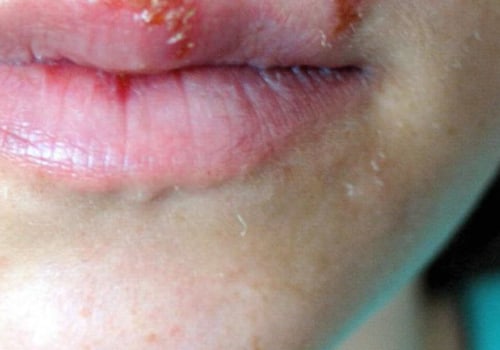
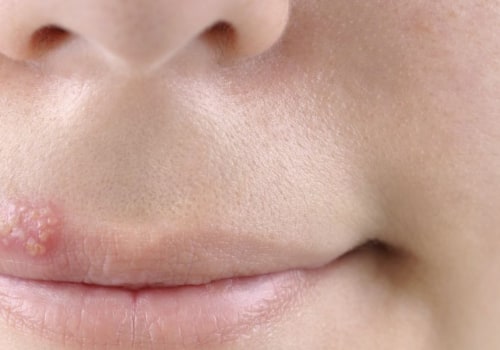
- Symptoms of genital herpes vary from person to person. Some people may have no symptoms at all, while others may experience a burning sensation during urination, small red bumps or blisters in the genital area, and itching or tingling in the area.In some cases, pain in the legs or buttocks may also occur.
How it is Spread
- Genital herpes is spread through direct contact with an infected person’s skin lesions or through sexual contact with an infected person. It can also be spread from mother to child during childbirth.Potential Complications
- Genital herpes can cause a number of serious complications, including neurological problems such as meningitis, vision problems, and an increased risk of HIV infection. It can also lead to infertility in women.Preventive Measures
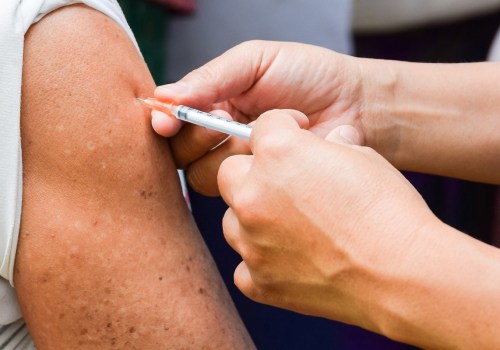
- To reduce the risk of transmission, it is important to use condoms during sexual activity, avoid contact with an infected person’s skin lesions, and get vaccinated against HSV if possible. In addition, it is important to practice good hygiene and wash hands frequently.Treatment for Genital Herpes
- Treatment for genital herpes typically includes antiviral medications and topical treatments.These medications can help reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks and help prevent future outbreaks. In some cases, doctors may also prescribe other medications to reduce inflammation and pain.
When to See a Doctor
- Anyone who suspects they may have genital herpes should see a doctor for testing and treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment are important for managing symptoms and reducing the risk of transmission.Types of HSV
Genital herpes is caused by two types of herpes simplex virus (HSV): HSV-1 and HSV-2.Both types of HSV can be spread through direct contact with an infected person, including sexual contact or through saliva. HSV-1 is typically associated with oral herpes, while HSV-2 is usually associated with genital herpes.It is important to note that both types of HSV can be transmitted through any type of contact, including skin to skin contact. HSV-1 is spread through contact with saliva, such as kissing or sharing utensils, cups, or other items. It can also be spread through contact with the infected area of the skin, such as a cold sore. HSV-2 is typically spread through sexual contact, but it can also be spread through skin-to-skin contact with an infected area of the body.
Reducing the Risk of Transmission
Genital herpes is a highly contagious sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is essential to take proper precautions in order to reduce the risk of infection.The most important way to prevent the spread of genital herpes is to practice safe sex. This includes using condoms every time you have sexual contact, as this will reduce the risk of transmitting the virus. It is also important to avoid contact with an infected person’s skin lesions, as this can also spread the virus. Individuals who are diagnosed with genital herpes should also inform their partners about their infection and practice safe sex to reduce the risk of transmission.
It is important to talk to your partner and make sure they understand how serious genital herpes can be. In addition, individuals should practice good hygiene to reduce the risk of transmission. This includes washing hands frequently, avoiding contact with infected areas, and not sharing items such as towels or clothing with someone who has genital herpes. Finally, individuals should see a healthcare provider regularly and get tested for genital herpes if they have any symptoms.
Early diagnosis and treatment of genital herpes can help reduce the risk of spreading the infection.
Treating Genital Herpes
Antiviral MedicationsAntiviral medications are the most common form of treatment for genital herpes. These drugs work by preventing the replication of the herpes virus and can reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. The most commonly prescribed antiviral medications are Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and Famciclovir. These medications can be taken orally or applied topically as a cream or ointment.It is important to take the prescribed dosage of these medications as directed by your doctor in order to maximize their effectiveness.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments for genital herpes can also be used to help reduce symptoms and prevent the spread of infection. These include creams and ointments containing ingredients such as tea tree oil, aloe vera, peppermint oil, and lemon balm. Topical treatments should be applied directly to the affected area several times a day until symptoms subside.Alternative Treatments
Some people may also choose to use alternative treatments for genital herpes, such as herbal remedies or nutritional supplements. However, it is important to consult your doctor before using any alternative treatments, as they may interact with other medications or have adverse side effects.Symptoms of Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is an STI caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).Common signs and symptoms of genital herpes infection may include painful blisters or sores on the genitals, itching or burning sensations in the genital area, and flu-like symptoms such as fever, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes. In some cases, there may be no visible symptoms at all. If symptoms do appear, they usually occur within two to three weeks after exposure to HSV. It is important to note that not everyone who is infected with HSV will experience symptoms. In fact, most people with genital herpes may not even realize they have it.
Additionally, some individuals may experience milder symptoms than others. It is also important to note that the symptoms of genital herpes can vary from person to person. The most common symptom of genital herpes is a cluster of small, red bumps or blister-like lesions on the genitals. These bumps may be painful and may burst open to form ulcers. The ulcers may take several weeks to heal.
Other possible symptoms include itching, burning, and pain in the genital area; pain during urination; and flu-like symptoms such as fever, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you suspect that you may have genital herpes. A healthcare provider can perform a physical exam and order tests to confirm a diagnosis. If you have been diagnosed with genital herpes, it is important to take steps to prevent its spread.
Complications of Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is a highly contagious sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is important to understand the potential complications associated with genital herpes in order to reduce the risk of infection.Complications of genital herpes can include physical and mental health issues, and can affect both men and women. Physical complications of genital herpes can include inflammation of the genitals, resulting in painful sores and blisters. These sores can be extremely painful, and can lead to significant discomfort. In some cases, these sores can become infected with bacteria, leading to further complications such as fever and swelling. If left untreated, genital herpes can also lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, which can cause infertility in women. Mental health complications associated with genital herpes are often overlooked.
Having a genital herpes infection can cause feelings of guilt, fear, anxiety, and depression. This is especially true for those who may have contracted the virus through sexual contact. It is important to seek out counseling and support to help cope with these emotions. It is important to understand how to prevent the spread of genital herpes in order to reduce the risk of infection. Practicing safe sex is the best way to avoid contracting or transmitting the virus.
This includes using condoms or other barrier methods during sexual activity, as well as avoiding sex with multiple partners. Additionally, it is important to avoid contact with any open sores on the genitals, as this can lead to transmission of the virus. Genital herpes is a highly contagious STI that can lead to physical and mental health complications. Understanding how to prevent the spread of genital herpes is the best way to reduce the risk of infection. Practicing safe sex, avoiding contact with open sores, and seeking out counseling and support are all important steps in preventing the spread of genital herpes. In summary, genital herpes is a highly contagious sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). This includes using condoms or other barrier methods during sexual activity, as well as avoiding sex with multiple partners. Additionally, it is important to avoid contact with any open sores on the genitals, as this can lead to transmission of the virus. Genital herpes is a highly contagious STI that can lead to physical and mental health complications. Understanding how to prevent the spread of genital herpes is the best way to reduce the risk of infection. Practicing safe sex, avoiding contact with open sores, and seeking out counseling and support are all important steps in preventing the spread of genital herpes. In summary, genital herpes is a highly contagious sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
To reduce the risk of transmission, it is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of genital herpes, get tested and treated if necessary, practice safe sex, and avoid contact with those who are infected. Prevention is key when it comes to reducing the risk of transmission, and understanding the complications associated with genital herpes can help motivate individuals to take preventive measures.